|
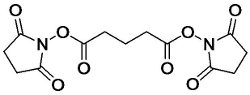
DSG crosslinker (Disuccinimidyl glutarate; Di(N-succinimidyl) glutarate) is a homobifunctional crosslinking reagent that is membrane permeable. DSG protein crosslinker is often used in ChIP assays to determine DNA-protein binding interactions; using DSG and formaldehyde in a two-step cross-linking strategy greatly improves the ChIP assay.
Region Capture Micro-C (RCMC) protocols using ProteoChem's DSG crosslinker are useful for enhancing changing protein/DNA interactions. ProteoChem's disuccinimidyl glutarate (DSG) is a bi-functional crosslinker that facilitates the capture of protein-DNA complexes by covalently linking primary amines on proteins to lysine residues on DNA. This capability is particularly advantageous in protocols like RCMC, which aims to map 3D genome architecture with high resolution. DSG's role in this context is to enhance the stability and capture efficiency of protein-DNA complexes during the crosslinking step. By forming covalent bonds between proteins and DNA, DSG ensures that transient or weak interactions are preserved, thereby improving the fidelity and depth of the resulting 3D genome maps.
DSG crosslinking takes place through amine-reactive NHS esters at both ends of a 5-atom (7.7 angstrom) spacer arm. DSG crosslinker must be dissolved in an organic solvent, such as DMSO or DMF, then added to an aqueous crosslinking reaction. The directly water soluble version of Di(N-succinimidyl) glutarate (DSG) is BS2G.
Specifications
Purity (NMR): ≥ 97%
Visual: White to off-white powder
Melting Point: 144-148ºC
Click here for: DSG Crosslinking Protocol & Product Information Sheet
Molecular weight: 326.26
Spacer Length: 7.7 Å
CAS Number: 79642-50-5
Alternative names: Di(N-succinimidyl) glutarate; Di-succinimidyl glutarate; Di N-succinimidyl glutarate; DSG Cross-linker; Bis-NHS glutarate; Disuccinimidyl glutaric dicarboxylate
Selected References:
Aboreden, N. G., Lam, J. C., Goel, V. Y., Wang, S., Wang, X., Midla, S. C., ... & Blobel, G. A. (2025). LDB1 establishes multi-enhancer networks to regulate gene expression. Molecular Cell, 85(2), 376-393.
Oh, S., Shao, J., Mitra, J., Xiong, F., D’Antonio, M., Wang, R., ... & Rosenfeld, M. G. (2021). Enhancer release and retargeting activates disease-susceptibility genes. Nature, 595(7869), 735-740.
Lee, C., Guo, J., Zeng, W., Kim, S., She, J., Cang, C., ... & Jiang, Y. (2017). The lysosomal potassium channel TMEM175 adopts a novel tetrameric architecture. Nature, 547(7664), 472.
Madsen, J. G. S., Rauch, A., Van Hauwaert, E. L., Schmidt, S. F., Winnefeld, M., & Mandrup, S. (2017). Integrated analysis of motif activity and gene expression changes of transcription factors. Genome Research, gr-227231.
Zhang, Y. J., Caulfield, T., Xu, Y. F., Gendron, T. F., Hubbard, J., Stetler, C., ... & Petrucelli, L. (2013). The dual functions of the extreme N-terminus of TDP-43 in regulating its biological activity and inclusion formation. Human molecular genetics.
Choi, N. M., & Boss, J. M. (2012). Multiple Histone Methyl and Acetyltransferase Complex Components Bind the HLA-DRA Gene. PloS one, 7(5), e37554. PMID: 22701520
PMCID: PMC3365104
Siersbæk, M. S., Loft, A., Aagaard, M. M., Nielsen, R., Schmidt, S. F., Petrovic, N., ... & Mandrup, S. (2012). Genome-wide profiling of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ in primary epididymal, inguinal, and brown adipocytes reveals depot-selective binding correlated with gene expression. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 32(17), 3452-3463.
Special bulk pricing is available on bulk quantities of DSG crosslinking reagent for your large volume manufacturing application.
|

